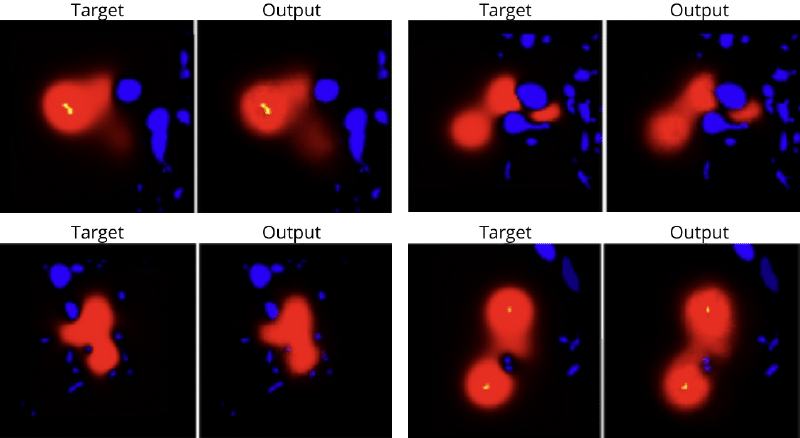
Description
We introduced an approach to estimate the heat induced tissue death in percutaneous thermal ablation based on a chained NCA architecture. While not directly producing a heat map, it accurately estimates cell death induced by thermal damage by implicitly modeling temperature field effects and evolution, going beyond heat distribution, with low root mean square error and high speed. The model is computationally efficient, characterized by a mere 12,210 learned parameters, and is capable of operating on a standard desktop computer due to its implementation through basic 3D convolutions. It can compute 25 minutes of treatment at a frequency up to 476 fps, making it suitable for interactive simulations and optimization loops.
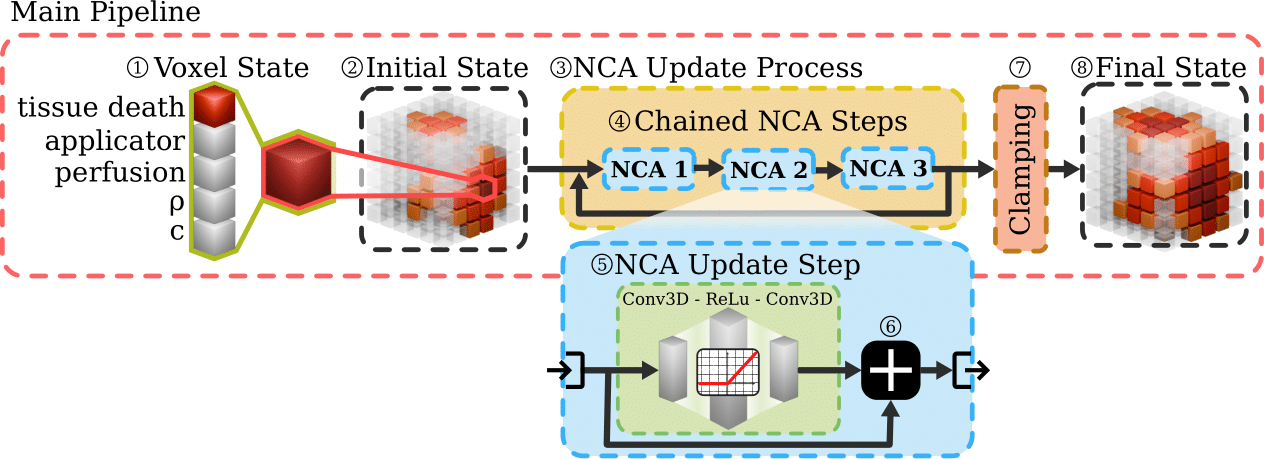
Model Architecture
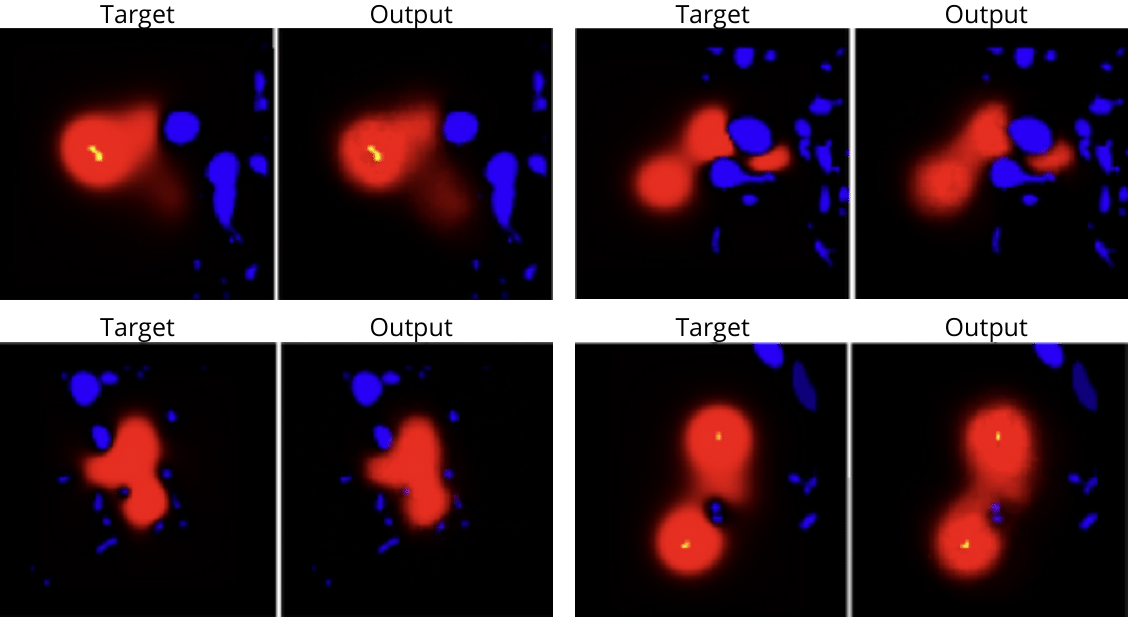
Target Output Pairs